SEO is one of the most effective digital marketing channels today because most consumers search on Google before making a purchase decision. Websites that appear on the first page of Google (Top 10 results) gain a massive advantage in visibility, trust, and sales conversions.
To understand how SEO works effectively, it is essential to first understand how Google ranks keywords and what factors influence search rankings.
How Google Collects Data and Ranks Search Results (In-Depth Explanation)
Before any website can appear on Google for a keyword, it must pass through a three-stage evaluation system. Each stage plays a critical role in determining whether a page is eligible to rank—and how high it can appear in search results.
Understanding this process is essential for building an SEO strategy that aligns with how Google actually works.
1. Crawling – How Google Discovers Web Content
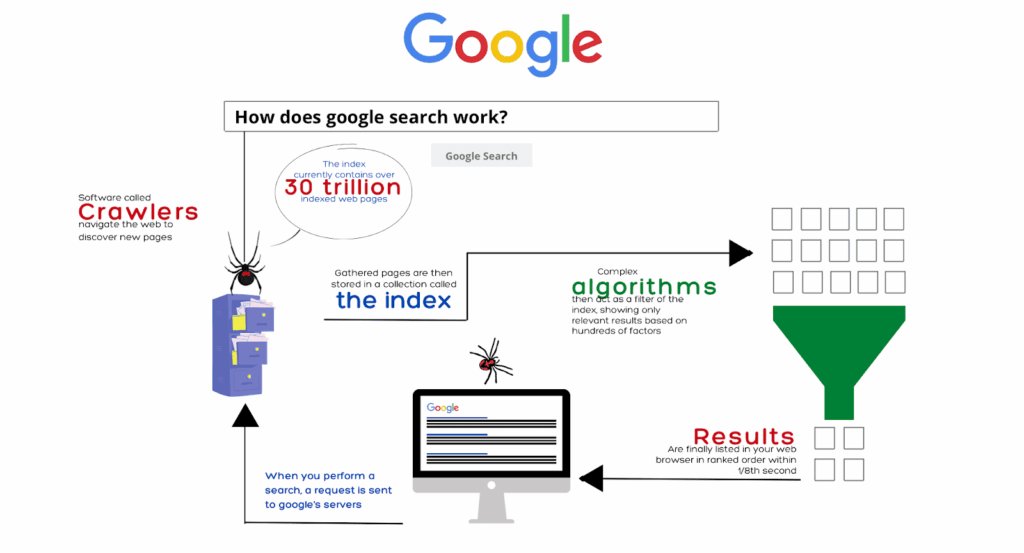
Crawling is the process by which Google discovers new and updated pages on the internet. To do this, Google uses automated programs called Googlebot (also known as crawlers or spiders).
How Googlebot Finds Pages
Googlebot navigates the web by following links, including:
- Internal links within a website
- External backlinks from other websites
- XML sitemaps submitted via Google Search Console
- Website navigation structures (menus, breadcrumbs, pagination)
Each link acts as a pathway that allows Googlebot to move from one page to another.
Why Crawling Matters for SEO
If Google cannot crawl a page, it cannot index or rank it. Common crawling issues include:
- Broken internal links
- Orphan pages (pages with no links pointing to them)
- Incorrect robots.txt rules
- Noindex or blocked resources
- Poor site architecture
A well-structured website makes it easier for Googlebot to crawl content efficiently, especially on large or content-heavy websites.
Learn more about our website design services.
2. Indexing – How Google Understands and Stores Content
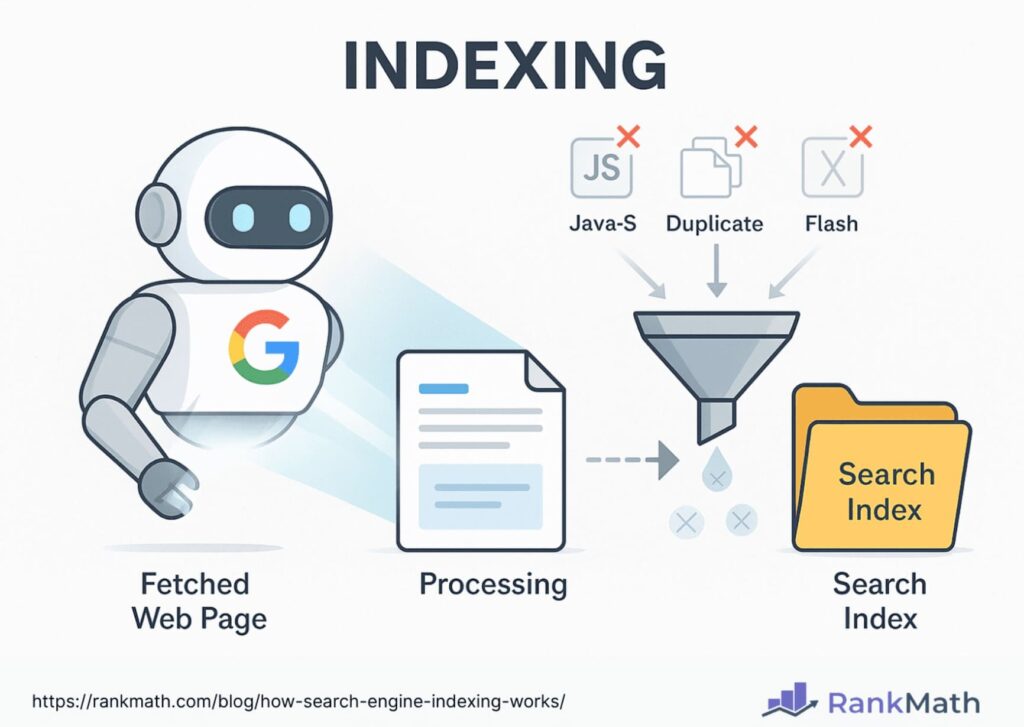
Once a page is crawled, Google attempts to understand what the page is about. This process is called indexing.
During indexing, Google analyzes multiple elements of the page, including:
- Primary topic and subtopics
- Content context and meaning, not just exact keywords
- Semantic keyword relationships
- Images, videos, and other media
- Structured data (schema markup)
- Language, freshness, and originality
Google uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning systems to determine the true intent and value of the content.
Indexing Is Not Guaranteed
Not every crawled page is indexed. Google may choose not to index pages that:
- Are duplicate or near-duplicate
- Offer little or no original value
- Are thin or auto-generated
- Contain spam or manipulative signals
Only indexed pages are eligible to appear in search results.
See More: Best Web Developer Singapore | Build Fast, Secure & SEO-Friendly Websites
3. Ranking – How Google Selects the Best Results
When a user submits a search query, Google’s ranking systems work in real time to decide which pages appear—and in what order.
To do this, Google must:
- Filter billions of indexed pages that could potentially match the query
- Evaluate relevance based on search intent and content alignment
- Assess quality signals, such as authority, trust, and user experience
- Rank results from most helpful to least helpful
Ranking Is About Intent, Not Keywords
Google does not rank pages simply because they contain a keyword. Instead, it ranks pages that:
- Best match the search intent (informational, transactional, navigational)
- Provide the most useful and complete answer
- Demonstrate expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T)
- Deliver a positive user experience
This is why two pages targeting the same keyword can rank very differently.
Key Factors That Influence Google Keyword Rankings (In-Depth Analysis)
Google does not rely on a single factor to rank keywords. Instead, it evaluates hundreds of signals that collectively determine which pages deserve top positions. These signals can be grouped into several core ranking categories, each playing a distinct role in search visibility and long-term performance.
1. Website Authority & Trust (The Evolution of PageRank)
PageRank was originally Google’s foundational algorithm, measuring the importance of a page based on the quantity and quality of links pointing to it. While Google no longer displays PageRank publicly, the concept remains deeply embedded in modern ranking systems.
Today, authority and trust are evaluated through a broader lens, including:
- Overall website credibility
- Quality and relevance of inbound links
- Brand recognition and mentions
- Content accuracy and reliability
High-authority websites are more likely to rank because Google trusts them to deliver reliable and safe information. Trust is built over time through consistent quality, ethical SEO practices, and positive user interactions.
2. Domain Factors and Their Modern Role
Domain-related signals still influence rankings, though far less than in early SEO days.
Key domain signals include:
- Domain age: Older domains with consistent publishing history tend to be more stable.
- Domain history: Clean, spam-free histories are essential.
- Keyword relevance in the domain name: Helpful when used naturally, but no longer a shortcut to rankings.
Modern priority order:
- Strong, recognizable brand domains
- Aged domains with clean link profiles
- Keyword-relevant domains used legitimately
Exact-match domains alone no longer provide ranking advantages and can even trigger spam signals if abused.
See More: Website Design Price Guide 2025 | How Much Does It Really Cost?
3. Content Quality – The Most Important Ranking Factor
Content quality is the core foundation of Google rankings.
High-performing content must:
- Fully satisfy search intent
- Provide depth, accuracy, and practical value
- Be original and non-duplicated
- Demonstrate real expertise and experience (E-E-A-T)
Google’s Helpful Content System actively suppresses content that exists only to manipulate rankings rather than help users. High-quality content, on the other hand, earns stable and long-lasting visibility.
4. Backlinks – Links as Signals of Trust and Authority
Backlinks function as endorsements from other websites. However, Google evaluates links based on quality rather than quantity.
Key backlink evaluation factors include:
- Relevance between the linking site and your content
- Authority and trustworthiness of the linking domain
- Natural anchor text patterns
- Diversity of referring domains
A few authoritative, relevant backlinks can significantly outperform hundreds of low-quality or spammy links.
5. Organic Traffic and User Engagement Signals
Google closely monitors how users interact with search results.
Important behavioral signals include:
- Click-through rate (CTR) from search results
- Time spent on the page
- Bounce behavior and pogo-sticking
- Repeat visits and engagement depth
When users engage positively with a page, Google interprets this as a signal that the content meets expectations and deserves higher visibility.
6. User Experience & Technical Performance
Google prioritizes websites that deliver seamless and enjoyable experiences.
Key UX and performance factors include:
- Fast page loading speed
- Mobile-friendly design
- Secure HTTPS encryption
- Logical site structure and navigation
- Clean, accessible code
Even high-quality content may struggle to rank if technical SEO issues hinder usability or performance.
See More: Top Tips for Website Design in Singapore: Boost Your Business Online
7. Conversion Signals and Business Value
Although conversions are not direct ranking factors, they reflect:
- Relevance to user needs
- Quality of content and design
- Overall user satisfaction
Pages that convert well tend to maintain stronger engagement metrics, which indirectly support SEO performance over time.
8. Social Signals – Indirect but Influential
Social engagement does not directly impact rankings, but it plays an indirect role.
Content that is widely:
- Shared
- Discussed
- Commented on
…tends to attract more visibility, backlinks, and brand awareness, all of which strengthen SEO signals organically.
Looking for a professional website that converts visitors into customers?
Our team provides professional website design services in Singapore tailored to your business goals.
Contact us to schedule a free consultation and explore the right solution for your brand.
Why SEO Is a Long-Term Strategy
Unlike paid advertising, SEO is not instant—but it is sustainable.
SEO:
- Requires time (typically 3–12 months)
- Builds durable keyword rankings
- Generates consistent organic traffic
- Is resistant to click fraud
- Continues delivering results even after optimization efforts slow
A well-executed SEO strategy compounds in value, making it one of the highest-ROI digital marketing channels available.
How does Google decide keyword rankings?
Google determines keyword rankings through a complex algorithm that prioritizes relevance, quality, and user satisfaction. The process involves analyzing hundreds of signals from queries, content, and user behavior to rank pages effectively.
Key Ranking Signals
Google first interprets the meaning of a query using natural language processing, correcting spelling and recognizing synonyms to match intent. Content relevance is assessed by keyword presence in headings and text, plus related elements like images or videos. Usability factors, such as page quality and source expertise, further refine rankings.
Algorithm Factors
Over 200 ranking factors are grouped into relevance (matching search intent), quality (authority and trustworthiness), and functionality (speed, mobile-friendliness). Freshness matters more for news queries, while backlinks and interaction data signal overall value. Weights vary by query type.
Ongoing Updates
Google updates its algorithm based on webmaster actions and user signals to combat low-quality content. Machine learning refines relevance estimates from anonymized data. Rankings fluctuate with competitors, updates, and evolving intent.
Does domain age still matter?
Domain age is not a direct ranking factor in Google’s algorithm. Google representatives, including John Mueller, have repeatedly confirmed this, emphasizing content quality, relevance, and backlinks over mere registration length.
Indirect Benefits
Older domains often accumulate more high-quality backlinks, trust signals, and content history over time, which can indirectly boost rankings. New domains may face a temporary “sandbox” effect where visibility is limited until Google assesses trustworthiness.
Current Relevance
As of 2026, focus remains on E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authoritativeness, trustworthiness) and user signals rather than age alone. New sites with superior content can outrank older ones.
Are backlinks still important?
Backlinks remain one of the top Google ranking factors in 2026.
Core Importance
They function as votes of confidence from other sites, transferring authority and signaling content trustworthiness to Google’s algorithm. High-quality, relevant backlinks from authoritative domains boost rankings more than quantity alone, as confirmed by studies showing top pages have 3.8x more links.
Quality Over Quantity
Focus on links from niche-relevant, high-traffic sites with natural anchor text, which also drive referral traffic and improve engagement metrics that indirectly aid SEO. Spammy or low-value links can harm rankings via penalties.
Evolving Role
Even with AI-driven search and E-E-A-T emphasis, backlinks correlate strongly with higher positions, faster indexing, and long-term visibility.
See More: How to Check Website Credibility Using Quick Online Tools
Can new websites rank on Google?
Yes, new websites can rank on Google, often within months if optimized correctly.
Ranking Feasibility
Google’s algorithm does not penalize new sites outright; it evaluates them based on content relevance, E-E-A-T signals, and technical quality rather than age. Recent 2026 SEO guides confirm new domains rank by demonstrating topical authority through focused content clusters and clear site identity from day one.
Success Strategies
Prioritize niche-specific content, internal linking, fast Core Web Vitals, and mobile optimization to accelerate indexing and visibility. Backlinks help but aren’t required initially—superior, intent-matched content outperforms older sites lacking depth.
Realistic Timeline
Expect impressions in 30 days, keyword positions by 90 days, and conversions by four months with consistent publishing and monitoring via Search Console.
Does Google favor long articles?
Google does not directly favor long articles over shorter ones as a standalone ranking factor. Instead, content depth and comprehensiveness matter when they better match user intent, often requiring more words for complex topics.
Correlation Evidence
Studies show top-ranking pages average 1,400-2,000 words because longer content tends to cover topics more thoroughly, attract backlinks, and improve dwell time—indirect ranking signals. However, superficially padded long-form content underperforms quality concise pieces.
Modern Priorities
In 2026, Google’s focus remains on E-E-A-T, entity relationships, and user satisfaction metrics rather than raw length. Shorter, expert-driven answers can rank highly for simple queries, while depth wins for informational ones.
Learn more about our website design services.
How long does SEO take to work?
SEO typically takes 3-12 months to show meaningful results, depending on factors like site age, competition, and strategy quality.
Early Phase (0-3 Months)
Initial progress includes indexing, impressions in Search Console, and minor keyword shifts from technical fixes and content publishing. New sites may see visibility in 30-90 days with focused optimization, though traffic remains low.
Growth Phase (4-6 Months)
Expect rising organic traffic, keywords entering top 50 positions, and first conversions as Google assesses authority through backlinks and engagement. Consistent content updates accelerate this for most sites.
Maturity Phase (7-12 Months)
Significant rankings in top 10, steady traffic growth (often 2-5x), and ROI emerge here, with compounding effects from prior efforts. High-competition niches may extend to 18 months.
What is the biggest SEO mistake?
Ignoring search intent is widely regarded as the biggest SEO mistake in 2026. Optimizing for the wrong user needs leads to high bounce rates, poor engagement, and demotion by Google’s algorithms focused on satisfaction metrics.
Why It Harms Most
Content mismatched to what searchers actually want—for example, promotional pages for informational queries—undermines E-E-A-T signals and wastes crawl budget on irrelevant pages. This foundational error amplifies other issues like thin content or keyword stuffing.
Quick Fixes
Conduct intent analysis using competitor SERP reviews and tools like “People Also Ask.” Rewrite top pages to align with transactional, informational, or navigational goals, then monitor via Search Console for improved dwell time.
See More: Best Professional Web Design Services in Singapore

