In 2026, on-page SEO optimization remains the foundation for ranking higher on Google and attracting the right audience. It refers to the process of refining every element on a web page — both visible content and the underlying HTML code — to boost search visibility and deliver a seamless user experience.
What is On-Page SEO Optimization?
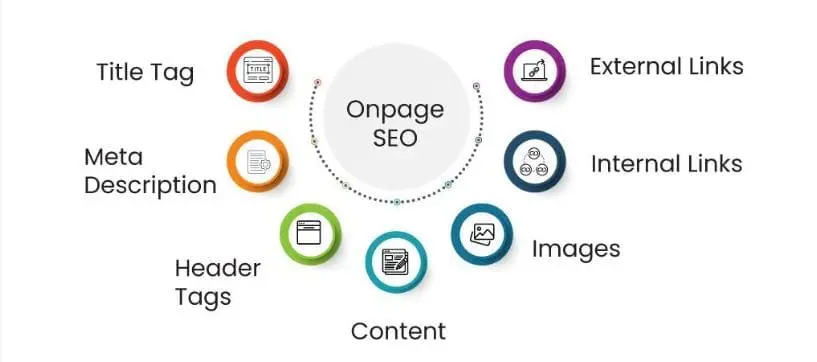
On-page SEO optimization is the process of improving individual web pages so they rank higher on search engines and deliver a better experience for users. It focuses on the elements you can control directly on your website — from visible content like text, headings, images, and links, to technical factors such as HTML structure, meta tags, and site performance.
Unlike off-page SEO, which relies on external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO gives you full control over how search engines interpret your content and how visitors interact with your site.
Key Elements of On-Page SEO Optimization
Keyword Research and Placement
Keyword research and placement is the foundation of effective on-page SEO optimization. Without targeting the right keywords, even the most well-designed page will struggle to attract relevant traffic.
How to Conduct Keyword Research
- Identify Primary Keywords: Choose a main keyword that directly reflects the core topic of your page. Example: “on-page SEO optimization.”
- Find Secondary and Related Keywords: Use synonyms, variations, and semantic (LSI) keywords to provide context. Example: “on-page SEO techniques,” “SEO page factors,” “how to optimize content for SEO.”
- Analyze Search Intent: Determine whether users want informational, navigational, or transactional content. Align your keywords with their intent.
- Leverage SEO Tools: Platforms like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush help evaluate search volume, keyword difficulty, and competition.
- Study Competitors: Review top-ranking pages to understand what keywords they target and how they structure their content.
Content Optimization
Content optimization is at the heart of on-page SEO optimization. High-quality content that aligns with user intent not only ranks better but also builds trust and keeps visitors engaged.
How to Optimize Content for SEO
- Match Search Intent: Every piece of content should answer the exact questions users are searching for. Identify whether the intent is informational (learning), navigational (finding), or transactional (buying).
- Create Comprehensive Content: Cover topics in depth to become a go-to resource. Long-form guides, detailed tutorials, and expert insights often perform better in search results.
- Use Structured Formatting: Break content into short paragraphs, bullet points, and numbered lists. This improves readability and helps search engines understand the hierarchy of information.
- Incorporate Query-Based Content: Add sections like FAQs, “People Also Ask” answers, or common troubleshooting tips to capture a wider range of searches.
- Add Multimedia Elements: Support your text with images, infographics, charts, or videos to enhance engagement and retention.
Best Practices for Content Optimization
- Keyword Integration: Place primary and secondary keywords naturally throughout the content. Emphasize them in introductions, subheadings, and conclusions.
- Readability: Aim for clear, simple language. Tools like Hemingway or Grammarly can help refine sentence structure and tone.
- Unique Value: Avoid duplicate or thin content. Provide original perspectives, case studies, or examples that differentiate your page from competitors.
- Content Freshness: Regularly update statistics, examples, and links to keep your content relevant and trustworthy.
- Engagement Signals: Encourage interaction through comments, calls-to-action (CTAs), and internal linking to related content.
Why It Matters
Optimized content not only improves search rankings but also increases dwell time, lowers bounce rates, and boosts conversion potential. In short, valuable content is the engine that drives both SEO performance and user satisfaction.
Title Tags & Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are two of the most critical on-page SEO elements. They act as the “first impression” of your content in search engine results and directly influence both rankings and click-through rate (CTR).
Title Tags
- Definition: The title tag is an HTML element that defines the page’s title. It’s displayed as the clickable headline in search results.
- Best Practices:
- Keep titles between 50–60 characters to avoid truncation.
- Place your primary keyword near the beginning of the title.
- Ensure every page has a unique title tag that clearly reflects its content.
- Make titles compelling and actionable, using power words like “guide,” “best,” “tips,” or “2026.”
- Example: “The Complete Guide to On-Page SEO Optimization in 2026”
Meta Descriptions
- Definition: A meta description is the brief summary (about 150–160 characters) shown beneath the title tag in search results. While it doesn’t directly affect rankings, it strongly impacts CTR.
- Best Practices:
- Keep descriptions under 160 characters so they display fully.
- Include your target keyword naturally to signal relevance.
- Write in a way that answers the searcher’s intent and sets clear expectations.
- Use a call-to-action (CTA) like “Learn more,” “Discover,” or “Start today.”
- Example: “Boost your rankings in 2026 with on-page SEO optimization. Learn proven strategies for content, keywords, and site performance.”
Why They Matter
- SEO Impact: Search engines use title tags as a strong ranking factor. Meta descriptions, while not direct ranking signals, influence user behavior and indirectly improve performance through higher CTR.
- User Impact: Both elements guide searchers to decide whether your page answers their query. Well-crafted titles and descriptions can significantly increase organic traffic even if your page isn’t ranked #1.
See More: Website UI Design Explained: 4 Golden Rules for a Stunning & User-Friendly Interface
Heading Tags
Heading tags (H1, H2, H3, and beyond) provide structure and hierarchy to your content. They not only guide readers through your page but also help search engines understand the context, relationships, and importance of different sections.
Importance of Heading Tags
- For Users: Headings break up long text into digestible chunks, improving readability and user experience. Clear headings allow readers to scan and find the information they need quickly.
- For Search Engines: Headings act as signals that highlight key topics and subtopics. By analyzing them, search engines can better determine what your page is about and rank it accordingly.
Best Practices for Heading Tags
1, H1 Tag (Main Title):
- Each page should have only one H1.
- It should describe the main topic and include the primary keyword.
- Example: “The Complete Guide to On-Page SEO Optimization in 2026”
2, H2 Tags (Subheadings):
- Use H2 tags for major sections of your content.
- Naturally integrate secondary keywords.
- Example: “Key Elements of On-Page SEO Optimization”
3, H3 Tags (Supporting Points):
- Use for subtopics under H2 sections.
- Provide additional detail or break down complex points.
- Example: under an H2 “Content Optimization,” use H3 like “Why Search Intent Matters” or “How to Use FAQs for SEO.”
4, H4–H6 Tags (Optional):
- Rarely needed but can be used for further breakdowns (e.g., lists within lists).
- Maintain logical hierarchy—never skip levels (H2 → H3 → H4).
Additional Tips
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Use headings to provide clarity, not just to repeat keywords.
- Write for Humans First: Make headings descriptive, informative, and engaging.
- Enhance Skimmability: Many readers scan headings before committing to reading full content. Strong headings can keep them engaged.
- Use Query-Style Headings: Incorporating questions (e.g., “What is On-Page SEO Optimization?”) helps capture traffic from voice search and Google’s “People Also Ask” boxes.
Why Heading Tags Matter
A clear heading structure ensures that your page is easy to navigate, improves accessibility, and reinforces topical relevance for search engines. In short, headings are the roadmap of your content—they guide both users and crawlers to the destination.
Internal Linking
Internal linking is the practice of connecting one page of your website to another through hyperlinks. It’s a critical part of on-page SEO optimization because it guides users, helps search engines discover content, and distributes authority (link equity) across your site.
Why Internal Linking Matters
- Improves Navigation: Internal links act as a roadmap, leading visitors to related content and keeping them engaged longer.
- Boosts SEO Rankings: When high-authority pages link to newer or less visible ones, they pass on “link equity,” helping those pages rank better.
- Enhances Crawlability: Search engine bots use links to crawl your website. A strong internal linking structure ensures all important pages are indexed.
- Reduces Bounce Rate: By suggesting relevant content, you encourage users to explore more pages instead of leaving immediately.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
1, Use Descriptive Anchor Text:
Instead of generic phrases like “click here,” use keywords that describe the target page.
Example: “Learn more about content optimization for SEO.”
2, Link to Relevant Content:
Ensure links are contextually related. Irrelevant linking confuses users and weakens SEO value.
3, Prioritize Important Pages:
- Link often to cornerstone content (e.g., your main guides or product pages).
- These should act as hubs of authority on your site.
4, Maintain a Logical Structure:
Follow a “topic cluster” approach: one pillar page linked to multiple subtopic pages, and those subtopics linking back to the pillar.
5, Don’t Overdo It:
Too many links can overwhelm users and dilute link equity. Aim for a natural balance (typically 3–5 internal links per 1,000 words).
Example of Effective Internal Linking
Imagine you have a main article on “On-Page SEO Optimization”. Within that article, you can internally link to:
- “Keyword Research and Placement Best Practices”
- “How to Write SEO-Friendly Meta Descriptions”
- “The Role of User Experience in SEO”
This creates a network of related pages, reinforcing topical authority.
See More: Can ChatGPT Help You Create a Modern Website in 2025?
Image Optimization
Image optimization is a crucial element of on-page SEO optimization. Search engines cannot “see” images the way humans do, so they rely on metadata like file names, alt text, and surrounding content to understand them. Properly optimized images not only improve SEO but also enhance user experience and page performance.
Why Image Optimization Matters
- SEO Visibility: Well-optimized images can rank in Google Images, driving additional traffic.
- Accessibility: Alt text ensures visually impaired users can understand image content through screen readers.
- Page Speed: Compressed images reduce file size, leading to faster load times and better Core Web Vitals scores.
- User Engagement: High-quality, properly labeled visuals improve content clarity and keep readers engaged.
Best Practices for Image Optimization
1, Use Descriptive File Names:
Replace generic names like IMG001.jpg with keyword-rich, descriptive names.
Example: on-page-seo-optimization-guide.jpg
2, Add Alt Text:
Describe the image accurately and naturally include keywords when relevant.
Example: “Screenshot of on-page SEO optimization checklist for 2026.”
3, Choose the Right File Format:
Use JPEG for photos (smaller size), PNG for graphics with transparency, and WebP for modern, highly compressed images.
4, Compress File Sizes:
Use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or built-in CMS plugins to reduce file size without losing quality.
5, Responsive Images:
Ensure images adjust to different devices and screen sizes for mobile optimization.
6, Lazy Loading:
Enable lazy loading so images only load when they enter the user’s viewport, reducing initial load time.
7, Add Captions and Surrounding Context:
Captions help users (and search engines) understand the relevance of an image within the content.
Example of Optimized Image
Instead of:
- File name: IMG_1234.png
- Alt text: “image”
Use:
- File name: on-page-seo-optimization-steps.png
- Alt text: “Diagram showing key steps of on-page SEO optimization including keywords, content, and internal linking.”
URL Structure
URL structure plays a significant role in on-page SEO optimization. A well-crafted URL not only helps search engines understand what a page is about but also improves user trust and click-through rates. Clean, descriptive URLs are easier to read, remember, and share.
Why URL Structure Matters
- SEO Relevance: Search engines use URLs as a ranking signal. Including keywords in the URL reinforces topical relevance.
- User Experience: Short, clear URLs look more professional and encourage users to click.
- Shareability: Clean URLs are easier to copy, paste, and share across platforms.
- Crawl Efficiency: Simple structures help search engines crawl and index content more effectively.
Best Practices for URL Structure
1, Keep It Short and Simple:
- Limit URLs to essential words.
- Example: /on-page-seo-optimization instead of /seo/on-page-seo-optimization-guide-2026-best-practices.
2, Include Keywords:
- Use the primary keyword naturally in the URL.
- Avoid keyword stuffing or repeating the same word multiple times.
3, Use Hyphens, Not Underscores:
- Hyphens (-) are preferred because search engines treat them as word separators.
- Example: /seo-strategy not /seo_strategy.
4, Lowercase Letters Only:
- Stick to lowercase to avoid duplicate content issues.
- Example: /seo-tips not /SEO-Tips.
5, Avoid Stop Words & Unnecessary Parameters:
- Words like “and,” “the,” or long tracking codes make URLs messy.
- Example: /seo-basics is cleaner than /the-best-seo-basics-and-tips?id=123.
6, Reflect Site Hierarchy:
- Use a logical folder structure that matches your website architecture.
- Example: /blog/on-page-seo-optimization clearly shows the page belongs to the blog section.
7, Keep URLs Static (Not Dynamic):
Dynamic URLs with long strings of numbers or symbols (?id=1456) are harder for search engines and users.
Example of Optimized vs. Poor URL
Poor:
www.example.com/index.php?id_wca=4812&ref=seo
Optimized:
www.example.com/on-page-seo-optimization
Mobile Optimization

Mobile optimization is a vital part of on-page SEO optimization. With Google’s mobile-first indexing, search engines primarily evaluate the mobile version of a site to determine rankings. This means that if your website doesn’t perform well on mobile devices, your search visibility will suffer—even if the desktop version is excellent.
Why Mobile Optimization Matters
- Search Rankings: Google favors mobile-friendly websites. A poor mobile experience can directly harm SEO rankings.
- User Experience: Over half of all web traffic comes from mobile devices. Visitors expect fast, easy-to-use mobile sites.
- Conversion Rates: A seamless mobile experience leads to higher engagement and conversions, while slow or unresponsive pages drive users away.
Best Practices for Mobile Optimization
1, Responsive Design:
- Ensure your site automatically adapts to different screen sizes.
- Use flexible layouts, scalable images, and fluid grids.
2, Fast Loading Speed:
- Compress images, enable caching, and use a CDN.
- Minimize heavy scripts and unnecessary plugins.
3, Mobile-Friendly Navigation:
- Use simple menus, large tap targets (buttons/links), and avoid overcrowded layouts.
- Keep forms short and easy to complete on smaller screens.
4, Readable Text and Content Layout:
- Ensure fonts are legible without zooming.
- Break text into short paragraphs with enough spacing for readability.
5, Avoid Intrusive Pop-ups:
Google penalizes sites with pop-ups or interstitials that block content on mobile devices.
6, Test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool:
Regularly check your pages to ensure they meet Google’s mobile usability standards.
Example of Good Mobile Optimization
- Bad UX: A site where users have to pinch and zoom, buttons are too small to tap, and images load slowly.
- Good UX: A responsive site with clear menus, fast-loading visuals, and CTAs designed for thumb-friendly interactions.
Page Speed

Page speed is one of the most important factors in on-page SEO optimization. A fast-loading website improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, and is a direct ranking factor in Google’s Core Web Vitals. Even a one-second delay can drastically impact conversions and engagement.
Why Page Speed Matters
- SEO Rankings: Google uses site speed as a ranking signal. Faster pages are favored in search results.
- User Experience: Visitors expect instant access. Slow pages frustrate users and increase abandonment rates.
- Conversions: Studies show that faster load times directly lead to higher conversion rates.
- Mobile Performance: With mobile-first indexing, speed on smartphones and tablets is just as critical as desktop.
Best Practices for Page Speed Optimization
1, Optimize Images:
- Compress file sizes without losing quality (use tools like TinyPNG or Squoosh).
- Serve modern formats such as WebP for better compression.
2, Use Browser Caching:
Store static files (CSS, JavaScript, images) locally in the user’s browser so they don’t reload with every visit.
3, Minimize CSS, JavaScript, and HTML:
- Remove unnecessary code, whitespace, and comments.
- Combine files where possible to reduce HTTP requests.
4, Enable Content Delivery Network (CDN):
Distribute your site’s content across multiple servers worldwide to reduce latency.
5, Reduce Server Response Time:
Use reliable hosting and optimize your server configuration.
6, Implement Lazy Loading:
Load images and videos only when they are about to appear on the screen.
7, Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content:
Ensure the visible part of your webpage loads first, so users can start interacting immediately.
8, Monitor with Tools:
Use Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Lighthouse to identify bottlenecks and receive actionable suggestions.
Example of Impact
- A page that loads in 2 seconds retains visitors.
- A page that takes 5 seconds or more loses up to 40% of potential users.
User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) is a cornerstone of on-page SEO optimization. Google’s algorithms increasingly prioritize how visitors interact with your site. A well-designed UX not only keeps users engaged but also sends positive signals (like longer dwell time and lower bounce rates) that can improve rankings.
Why UX Matters for SEO
- Engagement Signals: Metrics such as time on page, pages per session, and bounce rate indicate to search engines whether your content satisfies user intent.
- Conversions: A frictionless UX makes it easier for visitors to take desired actions (sign up, purchase, contact, etc.).
- Accessibility: Good UX ensures content is usable by everyone, including people with disabilities.
- Trust & Brand Authority: A smooth, professional design builds credibility and user confidence.
Best Practices for Strong UX
1, Intuitive Navigation:
- Use a clear menu structure that reflects your site hierarchy.
- Keep navigation consistent across all pages.
- Add breadcrumbs so users know where they are on the site.
2, Clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs):
- Use visible, well-placed CTAs like “Download Guide,” “Get Started,” or “Contact Us.”
- Keep wording action-oriented and benefit-driven.
3, Readable Layout & Design:
- Use white space, headings, and bullet points to make content scannable.
- Stick to simple fonts and mobile-friendly sizes.
- Ensure contrast between text and background for accessibility.
4, Mobile-Friendly Experience:
- Design pages for thumb-friendly navigation.
- Avoid pop-ups that block the main content on smaller screens.
5, Interactive & Engaging Elements:
- Add videos, infographics, or FAQs to make content dynamic.
- Use internal links to keep users exploring related topics.
6, Core Web Vitals:
- Optimize for Google’s UX signals:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): Fast loading of main content.
- FID (First Input Delay): Quick responsiveness when users click or tap.
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): Stable layouts without elements jumping around.
Example of Good vs. Bad UX
- Bad UX: Cluttered design, tiny fonts, hidden CTAs, and confusing navigation.
- Good UX: Clean structure, easy-to-follow menus, fast load times, and CTAs that guide users toward the next step.
See More: Website Design Price Guide 2025 | How Much Does It Really Cost?
Why On-Page SEO Matters in 2026
In 2026, on-page SEO optimization is more important than ever. As search engines continue to evolve with advanced AI and machine learning, ranking signals are no longer just about keyword placement — they emphasize content quality, user experience, and trustworthiness.
1, Smarter Search Engines
Google’s algorithms are now designed to understand context, semantics, and user intent. This means that stuffing keywords is no longer effective. Instead, well-structured content with clear headings, optimized images, and clean URLs makes it easier for search engines to interpret your page.
2, Content Quality is King
With so much online competition, thin or duplicated content quickly gets filtered out. To rank, businesses must publish original, comprehensive, and engaging content that directly answers user queries. Long-form guides, FAQs, and practical resources tend to perform best.
3, User Experience Drives Rankings
Google Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS) emphasize the importance of fast load times, responsive design, and stable page layouts. A site that is mobile-friendly, easy to navigate, and provides a smooth experience will outperform a technically perfect site that frustrates users.
4, Competitive Advantage
Companies that consistently invest in on-page SEO build a long-term advantage. By focusing on keyword optimization, internal linking, and technical improvements, they secure higher positions in SERPs, attract more organic traffic, and reduce reliance on paid ads.
5, Alignment with E-E-A-T
Google increasingly values Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). On-page SEO practices like clear author bios, structured content, and helpful internal links support these signals, building credibility in both the eyes of users and search engines.
FQA
What are the latest strategies for creating user-focused on-page SEO in 2026
The latest strategies for creating user-focused on-page SEO in 2026 emphasize aligning SEO efforts closely with user intent, experience, and satisfaction. Key strategies include:
1, Deep Understanding of User Intent
Research and analyze what users genuinely want when they search. Create content that fully answers their questions and solves their problems rather than simply targeting keywords.
2, Create High-Quality, Informative, and Engaging Content
Content must be original, comprehensive, and easy to read. Use clear headings, bullet points, and multimedia like images or videos to enhance understanding and engagement.
3, Optimize for Page Experience
Ensure fast page load speed, mobile responsiveness, and a seamless, intuitive navigation experience. Google values user experience metrics like Core Web Vitals to rank pages.
4, Use Natural Language and Conversational Tone
Write your content in a natural, conversational style that resonates with human readers, especially factoring in voice search trends.
5, Answer Featured Snippet and People Also Ask Questions
Structure content to directly address typical user queries succinctly, increasing the chances of being selected for featured snippets or PAA boxes.
6, Leverage Internal Linking Thoughtfully
Guide users smoothly to related content on your site to enhance engagement and reduce bounce rates.
7, Accessibility and Usability
Make your site accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, ensuring good readability, appropriate color contrast, and navigable structure.
8, Incorporate User Feedback and Behavioral Data
Analyze user behavior on your site (dwell time, bounce rate) and adjust content or layout to better meet their needs and preferences.
9, Schema Markup for Enhanced Search Results
Implement structured data to help search engines better understand your content and enhance snippets, making listings more attractive to users.
10, Optimize for Mobile and Voice Search
Since many users access content on mobile or via voice assistants, tailor your content and SEO to these access points with concise, conversational answers and mobile-friendly design.
How do I effectively use schema markup to boost search visibility in 2026
To effectively use schema markup to boost search visibility in 2026, follow these key steps:
1, Select Relevant Schema Types
Choose schema types that match your content and business, such as Article, Product, Recipe, Event, FAQ, Local Business, Review, or Breadcrumb. Using appropriate schema helps search engines understand exactly what your content is about.
2, Use Structured Data to Enhance SERP Features
Implement schema to increase your chances of rich results like featured snippets, knowledge panels, carousels, and FAQs, which improve click-through rates and visibility.
3, Implement FAQ and How-To Schema
FAQ and How-To schema are popular for directly answering user questions in search results, providing immediate value and drawing clicks.
4, Embed Schema in JSON-LD Format
Use JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) as recommended by Google—it’s easier to implement and maintain without interfering with page content.
5, Ensure Schema Accuracy and Completeness
Include all required and recommended fields within your schema markup to avoid errors and maximize benefits. Tools like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool can help validate your markup.
6, Regularly Update Schema with Content Changes
Keep your schema markup up to date as you add or change content to ensure search engines have the latest information.
7, Use Schema for Local SEO
For local businesses, use Local Business schema with accurate NAP (Name, Address, Phone) details and geo-coordinates to enhance local search visibility.
8, Combine Schema with Other SEO Best Practices
Schema improves how search engines read your pages but works best alongside optimized content, good UX, fast loading times, and mobile-friendly design.
9, Monitor Performance through Search Console
Track how your schema-enhanced pages perform in Google Search Console and adjust your markups based on reported errors and enhancements.
How can I optimize page speed without harming content quality in 2026
To optimize page speed in 2026 without harming content quality, focus on these effective strategies:
1, Compress and Optimize Images
Use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or Squoosh to compress images without visible quality loss. Opt for next-gen formats such as WebP or AVIF, which offer smaller file sizes with high quality. Implement responsive images with the srcset attribute and prioritize loading images above the fold first. Use lazy loading to defer offscreen images until needed, reducing initial load time.
2, Minify and Compress Code
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files by removing unnecessary spaces, comments, and formatting. Enable server-side compression (Gzip or Brotli) to reduce the size of files transferred to users.
3, Defer or Asynchronously Load Non-Critical JavaScript
Delay loading scripts that aren’t essential for initial rendering using async or defer attributes to prevent blocking page rendering.
4, Remove Unused CSS and JavaScript
Identify and eliminate unused code, plugins, or third-party scripts that bloat your site. Tools like PurgeCSS and Chrome DevTools Coverage tab can help pinpoint unused code.
5, Use Browser Caching and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Enable caching so visitors’ browsers store static files locally for faster repeated visits. CDNs serve content from servers closest to the user, reducing latency.
6, Preload Key Resources
Use rel=”preload” to instruct browsers to prioritize loading important assets like hero images or critical scripts, improving perceived and actual load times.
7, Optimize Hosting and Server Response Time
Choose reliable hosting that matches your traffic and content needs. Enable server-side caching to serve pre-built pages faster.
8, Avoid Hosting Videos Locally
Host videos on dedicated platforms (e.g., YouTube, Vimeo) and embed them to reduce server load.
9, Maintain Content Quality
Ensure optimizing does not mean removing valuable content or media. Use optimization methods that preserve the user experience, such as high-quality compressed images and avoiding excessive script removal that could break functionality.

